Sports Nutrition: Carb Loading
Posted by Niamh Duffy | 3rd Oct 2023
Want to stay fueled for those powerful workouts? GourmetFuel is giving you all the tips and tricks to stay energised during your time of exercise. Whether it’s swimming, team sports or training for a race our nutrition ultimately affects our endurance and performance throughout.
The Importance of Macronutrients in our Diet
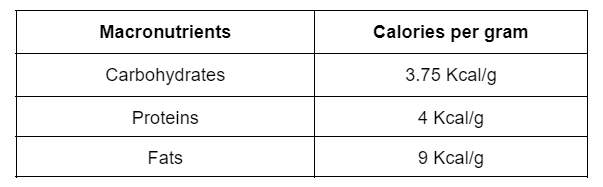
All forms of sports & exercise require energy and this derives from the nutrients consumed in our diet. Macronutrients creates ATP which is our ‘energy currency’ in the body, they are then broken down to yield different quantities of energy which is typically expressed into calories per gram consumed as follows:
Firstly, we must understand the main focus of carbohydrates to know when the optimal time is to consume them. Carbohydrate sources are essential for energy metabolism particularly for men and women, taking part in intense exercise as fatigue is associated with the decline of carbohydrate stores in the muscles.
Fats are also important to also include in the diet as they are typically dense sources of calories that provide energy during short & long duration exercise. Some fat sources can contain omega-3’s, which have anti-inflammatory properties that aid recovery, such as fatty fish, nuts and seeds.
Protein should be consumed as close to the training session as possible to allow for optimal muscle growth and repair. It also enhances protein synthesis, which is in its prime post exercise and can have a positive effect on muscle adaptation.
Carbohydrate Loading, What Is It?
This is a technique used leading up to a race or intense exercise to improve endurance and enhance performance. It is carried out to increase glycogen stores in the muscles to be used during the time of exercise. The general guidelines indicate to eat a carbohydrate heavy meal in the days leading up, which it is approximately recommended to have 7-10g per kg of body weight per day. It is not necessary to consume a carbohydrate load more than 36 hours before race/game day as the body of trained individuals have the ability to rapidly synthesise glycogen from high carbohydrate intake as training intensity declines right before a race.
Carbohydrates consumed in the 3-4 hour window before intense exercise will typically result in an increased & optimum endurance capability. This effectiveness is enhanced when no carbohydrate is ingested during the exercise. Typical examples should be a variety of sources such as fruit and vegetables while also including mainly simple carbohydrates i.e. bread, potatoes, pasta, and rice.
Recovery & Planning Ahead
All these macronutrients also play apart in recovery during rest days of individuals taking part in sport and exercise. Our appetite can vary in the days after an intense exercise period and therefore, it’s important to keep up nutrition during these days. Nutrition also has an effect on our mental performance, which is key for staying focused during these periods of intense exercise.
Take a look at our meal plans such as the high protein/low carb or alternatively our registered nutritionists can design a personalised plan to meet your needs. All plans have a nutrition summary available for each day of your plan. This will allow you to track macronutrients daily and plan your workouts to be tailored to each day of the week.
Reference -
Lanham-New, S. (2011) Sport and exercise nutrition. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell.
Smith-Ryan, A. and Antonio, J. (2013) Sports nutrition & performance enhancing supplements. Ronkonkoma, NY: Linus Learning.
